In the fast-paced world of software development, quality assurance (QA) is more than just testing—it’s about delivering reliable, efficient, and user-friendly software. With rising customer expectations and frequent release cycles, QA teams must be proactive in preventing defects, not just detecting them.
That’s where Six Sigma steps in.
Originally developed for manufacturing, Six Sigma is a proven, data-driven methodology designed to eliminate defects and improve process quality. When applied to software testing, Six Sigma provides a structured framework to enhance test planning, reduce defect leakage, and improve team efficiency.
In this guide, we’ll explore how Six Sigma in software testing can boost your QA strategy and what practical steps QA teams can take to apply it effectively.
Table of Contents

What is Six Sigma?
Why Use Six Sigma in Software Testing?
Core Principles of Six Sigma
The DMAIC Framework in QA
Practical Applications of Six Sigma in Testing
Benefits of Six Sigma in QA
Challenges in Applying Six Sigma
Best Practices for QA Teams
Backlog – Dev + QA Collaboration in One Platform
Six Sigma vs Traditional Testing Approaches
Final Thoughts
What is Six Sigma?

Six Sigma is a quality management methodology that aims to reduce variation and eliminate defects by using statistical tools and a structured process improvement cycle. It sets a goal of fewer than 3.4 defects per million opportunities—an extremely high standard of quality.
Core Concepts:
Data-driven decisions
Root cause analysis
Process improvement through iteration
Continuous quality monitoring
Why Use Six Sigma in Software Testing?

While software testing has traditionally focused on identifying bugs, Six Sigma introduces a preventive mindset, allowing QA teams to improve how and why defects occur rather than just detecting them post-facto.
Why it matters:
Reduces defect leakage in production
Improves test coverage and efficiency
Strengthens collaboration across QA and development
Creates measurable quality metrics and standards
Core Principles of Six Sigma

Six Sigma is founded on principles that align naturally with the QA discipline.
Six Sigma Principles:
Customer focus: Deliver what the end-user values most
Process orientation: Treat testing as a repeatable, measurable process
Data-driven decisions: Base improvements on empirical data, not assumptions
Defect prevention: Avoid defects before they reach the customer
Cross-functional collaboration: QA, Dev, and Product work together to improve outcomes
The DMAIC Framework in QA
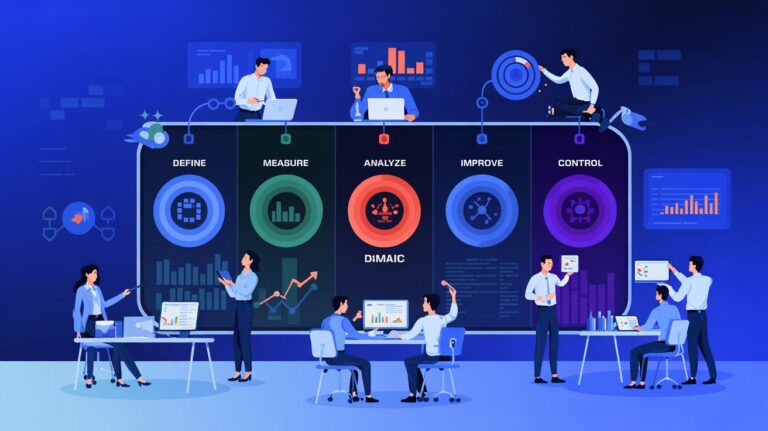

At the heart of Six Sigma lies the DMAIC methodology: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control. Each phase can be adapted to QA workflows to optimize software testing and quality.
🔸 Define
Clarify testing objectives and quality benchmarks.
Identify key problems in the current testing process
Set clear, measurable goals (e.g., reduce critical bugs by 30%)
Determine customer and stakeholder expectations
🔸 Measure
Gather data to assess current testing performance.
Track defect density, test execution time, and test pass rates
Record defect leakage and production failures
Use metrics like MTTR (mean time to resolve) and code coverage
🔸 Analyze
Examine collected data to identify root causes of defects.
Perform Root Cause Analysis (RCA) on recurring bugs
Use tools like Pareto Charts and Fishbone Diagrams
Spot gaps in test coverage or automation breakdowns
🔸 Improve
Implement solutions to eliminate root causes of defects.
Refine test cases and test data
Introduce automation or CI/CD improvements
Train testers on new tools and methodologies
🔸 Control
Establish controls to sustain quality improvements.
Set up quality gates in CI/CD pipelines
Monitor KPIs (e.g., defect leakage, release readiness)
Document changes and create regression baselines
Practical Applications of Six Sigma in Testing
Six Sigma isn’t just a concept—it can be embedded in day-to-day QA operations.
Where it fits:
Regression test planning and optimization
Analyzing flaky or failing automated test cases
Improving API testing reliability
Enhancing test data management
Reducing rework from misaligned requirements
Benefits of Six Sigma in QA

Implementing Six Sigma principles in QA can bring major value to teams and organizations.
Key Benefits:
📉 Fewer post-release defects
⏱️ Reduced test cycle time
📊 Improved visibility through KPIs
🤝 Better alignment with business goals
💰 Lower cost of quality
🧪 More reliable automated testing
🎯 Standardized testing practices across teams
Challenges in Applying Six Sigma

While beneficial, Six Sigma isn’t a silver bullet and can pose challenges in software settings.
Common Challenges:
Complexity in applying manufacturing models to dynamic software processes
Requires a culture of data discipline
Initial training and adoption can take time
Over-analysis may hinder fast-paced Agile teams
Not always suitable for small startups or MVP environments
Best Practices for QA Teams Using Six Sigma

Adopting Six Sigma in QA is easier when implemented gradually and thoughtfully.
Best Practices:
Start with a pilot—apply DMAIC to a single test module or defect cluster
Collect clean, reliable test data consistently
Encourage collaboration between QA, developers, and product managers
Combine Six Sigma with Agile/DevOps practices
Provide internal training or hire Six Sigma certified testers
Review and refine KPIs regularly
Six Sigma vs Traditional Testing Approaches

| Feature | Traditional Testing | Six Sigma in Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Detect bugs | Prevent defects |
| Methodology | Ad-hoc or scripted | Structured (DMAIC) |
| Data Usage | Reactive | Predictive & data-driven |
| Process Improvement | Occasional | Continuous |
| Tools | Test case management | RCA, control charts, Pareto analysis |
Six Sigma helps move testing from reactive to proactive, aligning QA goals with long-term product quality objectives.
Final Thoughts

In a world of continuous integration, rapid releases, and rising user expectations, QA must evolve. Six Sigma provides a powerful framework for reducing defects, improving processes, and delivering value to customers faster and more reliably.
By applying the DMAIC methodology and promoting a culture of quality, Six Sigma empowers QA professionals to do more than test—they lead the way in delivering better software.