Introduction

In today’s digital landscape, scalability and reliability are critical for any web application. Slow performance and downtime can result in poor user experience, lost revenue, and damage to brand reputation. Load testing helps prevent these issues by simulating real-world traffic and measuring system performance under different loads.
While Selenium is widely known for functional and UI testing, it can also be effectively used for load testing when integrated with tools like JMeter, Locust, or BlazeMeter. In this guide, we’ll explore how to leverage Selenium for load testing and ensure your application remains scalable and reliable.
What is Load Testing?

Load testing is a type of performance testing that evaluates how an application performs under expected and peak traffic conditions. The goal is to identify bottlenecks and ensure smooth operation during high user loads.
Key Benefits of Load Testing:
✅ Ensures the application can handle peak traffic without crashing.
✅ Identifies performance bottlenecks before they impact users.
✅ Helps optimize infrastructure and resource allocation.
✅ Improves application responsiveness and user experience.
Why Use Selenium for Load Testing?
Selenium, by itself, is not designed for load testing, but it can be combined with performance testing tools like:
Apache JMeter – A popular tool for performance and load testing, which can integrate with Selenium scripts.
BlazeMeter – A cloud-based load testing solution that extends JMeter’s capabilities.
Locust – A Python-based tool for distributed load testing that can work alongside Selenium.
Advantages of Using Selenium for Load Testing:
✔ Simulates real user interactions (clicks, form submissions, navigation).
✔ Supports multiple browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari).
✔ Works well with CI/CD pipelines for continuous performance monitoring.
How to Perform Load Testing with Selenium and JMeter

Step 1: Set Up Your Selenium Test Scripts
Start by creating a Selenium WebDriver script to automate user interactions with your web application. For example, a simple login test:
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get(“https://yourwebsite.com/login”);driver.findElement(By.id(“username”)).sendKeys(“testuser”);
driver.findElement(By.id(“password”)).sendKeys(“password123”);
driver.findElement(By.id(“loginButton”)).click();
Step 2: Convert Selenium Test to JMeter Script
Open JMeter and create a Test Plan.
Add a Thread Group (define user load and ramp-up time).
Use JMeter WebDriver Sampler to run Selenium scripts within JMeter.
Configure HTTP Requests to simulate traffic on different endpoints.
Set up Listeners (View Results Tree, Summary Report) to analyze test results.
Step 3: Execute Load Test & Analyze Performance Metrics
Run the test and monitor key metrics like response time, error rate, throughput, and server resource utilization.
Identify performance bottlenecks and optimize database queries, caching, or server configurations.
Best Practices for Effective Selenium Load Testing
✅ Optimize Test Scripts for Performance
Avoid unnecessary waits (use explicit waits instead of
Thread.sleep).Minimize DOM interactions to improve execution speed.
Run tests in headless mode for faster execution.
✅ Use Distributed Load Testing for Large Scale Applications
Run Selenium tests on a grid (e.g., Selenium Grid, Kubernetes) for better scalability.
Distribute load across multiple servers using BlazeMeter or Locust.
✅ Monitor System Performance During Load Testing
Track CPU, memory, and database usage to identify bottlenecks.
Use APM tools like New Relic, Datadog, or Prometheus for deeper insights.
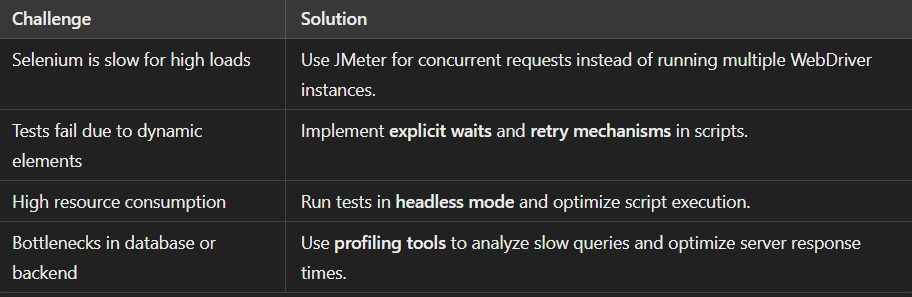
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Conclusion
Selenium load testing, when combined with tools like JMeter and BlazeMeter, helps ensure your application can handle real-world traffic effectively. By optimizing test scripts, distributing load across multiple servers, and monitoring key performance metrics, you can build scalable and reliable applications that provide a seamless user experience.