Continuous Integration (CI) is a cornerstone of modern software development and quality assurance, allowing teams to quickly and effectively integrate code changes into a shared repository several times a day. This practice significantly reduces integration issues, accelerates software delivery, and enhances overall code quality.
Table of Content
What is Continuous Integration?
Benefits of Continuous Integration
Key Principles of Continuous Integration
Best Practices for Implementing Continuous Integration
Tools for Effective Continuous Integration
Conclusion
Introduction

In today’s digital landscape, scalability and reliability are critical for any web application. Slow performance and downtime can result in poor user experience, lost revenue, and damage to brand reputation. Load testing helps prevent these issues by simulating real-world traffic and measuring system performance under different loads.
While Selenium is widely known for functional and UI testing, it can also be effectively used for load testing when integrated with tools like JMeter, Locust, or BlazeMeter. In this guide, we’ll explore how to leverage Selenium for load testing and ensure your application remains scalable and reliable.
What is Continuous Integration?

Continuous Integration is a development methodology where developers frequently merge their code changes into a central repository. Automated builds and tests are run upon each integration, providing immediate feedback on code functionality and integration errors. The primary goal is to identify and resolve integration issues early, thereby ensuring software quality and reliability.
Benefits of Continuous Integration
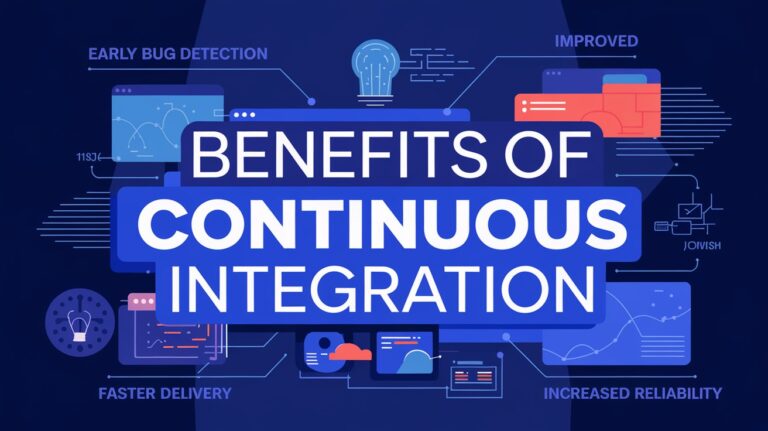
Implementing CI offers numerous advantages:
Early Bug Detection: Automated testing with each integration catches issues promptly, reducing the cost and effort required for fixes.
Enhanced Collaboration: Continuous integration fosters a culture of frequent, small commits, enhancing team collaboration and reducing conflicts.
Improved Software Quality: Regular integration and testing ensure that each component works harmoniously, delivering reliable and high-quality software.
Reduced Deployment Risk: Frequent code integrations minimize potential risks and simplify debugging processes.
Key Principles of Continuous Integration
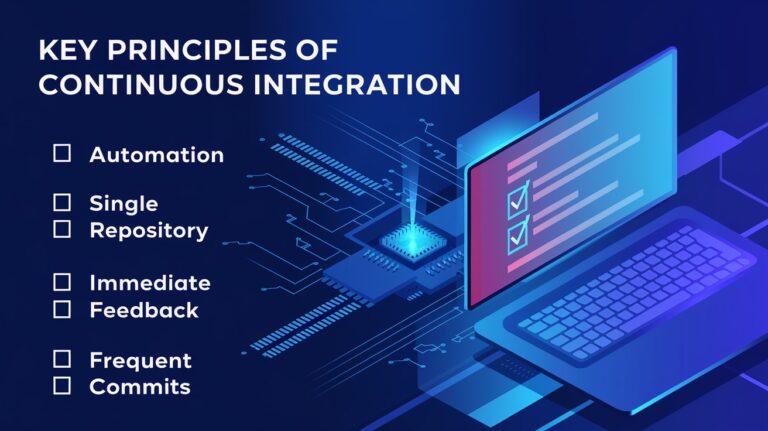
To leverage Continuous Integration effectively, teams should adhere to the following principles:
1. Maintain a Single Source Repository
Keep the project code in a single, shared repository accessible to all team members. This practice ensures consistency and simplifies management.
2. Automate the Build Process
Automation of the build process reduces manual errors and speeds up testing. Tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI help streamline this automation.
3. Frequent Code Commits
Developers should commit their code changes at least daily. Small, incremental updates make it easier to isolate and fix problems quickly.
4. Automated Testing
Incorporate automated unit, integration, and regression tests to immediately validate code changes. Tools such as Selenium, JUnit, or TestNG enhance the accuracy and coverage of testing.
5. Immediate Feedback
The CI process should provide immediate feedback on integration status, helping developers quickly address any issues.
Best Practices for Implementing Continuous Integration
Implementing Continuous Integration effectively requires adherence to certain best practices:
Clear Commit Messages: Ensure all code commits have clear and descriptive messages to simplify tracking changes.
Monitor and Maintain the Pipeline: Regularly monitor the CI pipeline for failures or performance issues. Quick intervention maintains workflow continuity.
Keep Tests Fast and Reliable: Optimize tests to execute quickly and reliably, providing timely and accurate feedback.
Branching Strategy: Use a simple, robust branching strategy like Git Flow or trunk-based development to reduce complexity.
Integrate Security Checks: Include automated security scans to identify vulnerabilities early in the development lifecycle.
Tools for Effective Continuous Integration

Leveraging the right tools accelerates CI adoption and enhances effectiveness:
Jenkins: Flexible, open-source CI server.
GitLab CI/CD: Integrated solution within GitLab repositories.
CircleCI: Cloud-native platform that scales efficiently.
Travis CI: Easy-to-use hosted solution suitable for open-source projects.
Conclusion
Continuous Integration revolutionizes the software development lifecycle by facilitating rapid integration and ensuring high-quality releases. Adopting robust CI practices reduces risks, enhances team collaboration, and improves overall software quality. As your team masters Continuous Integration, you’ll see clear gains in efficiency, reliability, and product delivery.
Integrating CI practices today sets the foundation for a competitive and agile software delivery process.